|
Line Graphs
Prerequisites
Bar
Graphs
Learning Objectives
- Create and interpret line graphs
- Judge a line graph would be a appropriate for a given dataset
A line graph is a bar graph with the tops of the
bars represented by points joined by lines (the rest of the bar
is suppressed). For example, Figure 1 was presented in the section
on bar charts and shows changes in the Consumer Price Index (CPI)
over time.

Figure 1. A bar chart of the percent change in the CPI over
time. Each bar represents percent increase for the three months ending at the
date indicated.
A line graph of these same data is shown in Figure 2. Although
the figures are similar, the line graph emphasizes the change
from period to period. 
Figure 2. A line graph of the percent change in the CPI over
time. Each line represents percent increase for the three months ending at the
date indicated.
Line graphs are appropriate only when both the X- and Y-axes
display ordered (rather than qualitative) variables. Although bar graphs can
also be used in this situation, line graphs are generally better at comparing
changes over time. Figure 3, for example, shows percent increases and decreases
in five components of the CPI. The figure makes it easy to see that medical costs
had a steadier progression than the other components. Although you could create
an analogous bar chart, its interpretation would not be as easy.
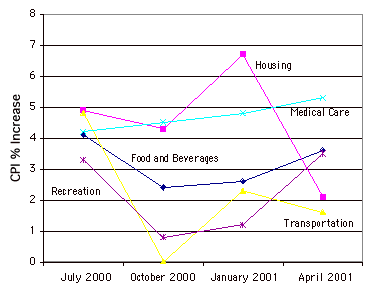
Let us stress that it is misleading to use a line graph when
the X-axis contains merely qualitative variables. Figure 4 inappropriately
shows a line graph of the card game data from Yahoo, discussed in the section
on qualitative variables. The defect in Figure 4 is that it gives the false
impression that the games are naturally ordered in a numerical way.

|