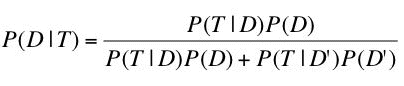
Bayes' Theorem
Bayes' theorem considers both the prior probability of an event and the diagnostic value of a test to determine the posterior probability of the event. The theorem is shown below:
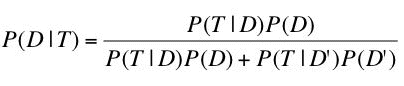
where P(D|T) is the posterior probability of condition D given test result T, P(T|D) is the conditional probability of T given D, P(D) is the prior probability of D, P(T|D') is the conditional probability of T given not D, and P(D') is the probability of not D'.