If you are having problems with Java security, you might find
this page helpful.
Learning Objectives
- Distinguish between simple random sampling and stratified sampling.
- Describe how often random and stratified sampling give exactly the same result.
Review of Sampling
Instructions
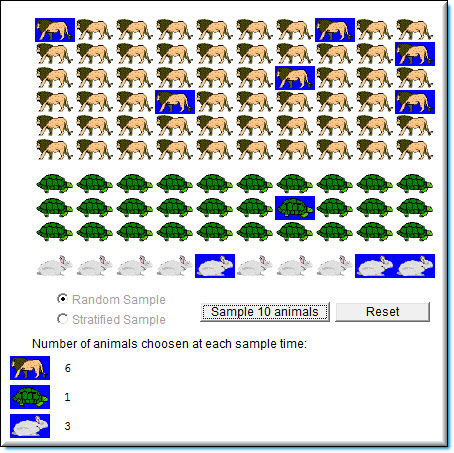
The sampling simulation uses a population of 100 animals: 60 lions, 30 turtles, 10 rabbits.
Options
 : This option allows you to draw a sample of 10 animals at a time with each animal having an equal chance of being selected.
: This option allows you to draw a sample of 10 animals at a time with each animal having an equal chance of being selected.
 : This option allows you to draw a sample of 10 animals at a time, with each number of animals from a group being proportional to their group’s size of the population.
: This option allows you to draw a sample of 10 animals at a time, with each number of animals from a group being proportional to their group’s size of the population.
Simulation Results
 | The number of animals chosen from each group when a sample is drawn is shown next to the picture of the animal. |
When you give it a try:
Random Sampling:
Stratified Sample:
Illustrated Instructions
The opening screen of the sampling simulation displays all 100 animals in the population.
You can select between a random sample and a stratified sample directly below the population and then generate a sample of ten animals.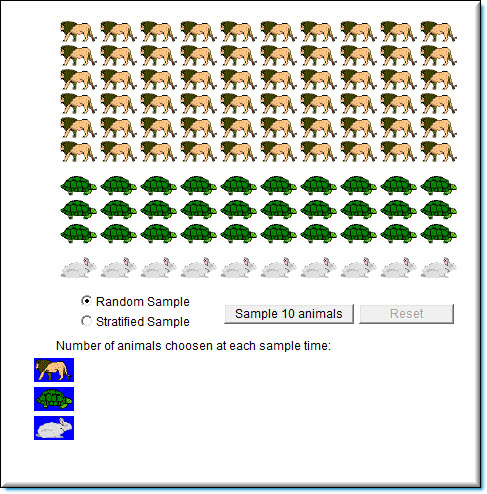
Below is an example of a random sample. Notice that animals selected are highlighted in the population and the total number of animals selected from each category is listed at the bottom of the simulation.