|
|
Variance Sum Law II
Author(s)
David M. Lane
Prerequisites
Variance
Sum Law I
Learning Objectives
- State the variance sum law when X and Y are not assumed to be independent
- Compute the variance of the sum of two variables if the variance of
each and their correlation is known
- Compute the variance of the difference between two variables if the
variance of each and their correlation is known
Recall that when the variables X and Y are independent,
the variance of the sum or difference between X and Y can be written
as follows:
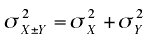
which is read "The variance of X plus or
minus Y is equal the variance of X plus the variance of Y.
When X and Y are correlated, the following formula
should be used:
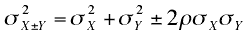
where ρ is the correlation between X and Y
in the population.
If the variances and the correlation are computed
in a sample, then the following notation is used to express the
variance sum law:
 . .
Please answer the questions:
|
|